About Customers
This topic provides an overview of customer licenses, including information about license types, the Customers page in the vendor portal, and how Replicated uses the customer entitlement information that you provide in license files.
Overview of Customer Licenses
Each customer that you create in the Replicated vendor portal has a unique license file. The customer uploads this license file to the Replicated admin console when they install or update your application.
They can also update, or sync, the license file from the admin console. For more information, see Updating licenses in the Enterprise documentation.
Each customer license includes several fields that uniquely identify the customer and the application, specify the release channel, and define the entitlement information about the customer.
Entitlement information describes the details of the license, such as if the license has an expiration date.
Replicated securely delivers these entitlements to the application and makes them available in the Kubernetes manifest files or at runtime using the Replicated admin console API.
License Types
Each customer license includes a license_type field. The type of customer defined
by the license_type field is used solely for reporting purposes. A customer's
access to your application is not affected by the type that you assign.
The possible values for the license_type field are development, trial, paid, and
community. For more information about each type, see About Customer License Types.
Built-in and Custom License Fields
Each customer license file has several built-in fields. Built-in fields are reserved field names. You can specify the values for these fields to define entitlements for the customer.
For example, there are built-in license fields that define the license expiration date, the customer name, the application slug value, and whether air gap installations are supported.
For more information about built-in fields, see About Built-in License Fields.
You can also create custom license fields. Custom license fields are useful when there are entitlements specific to the customer.
For example, you can create a custom license field to limit the number of active users permitted. Or, you can create a field that specifies the domain on which the customer can run the application.
For more information about creating custom license fields, see Managing Custom License Fields and Referencing Custom License Fields.
License Expiration Handling
The built-in expires_at license field defines the expiration date for a customer license. When you set an expiration date in the vendor portal, the expires_at field is set to midnight UTC on the date selected.
By default, an application with an expired license continues to run, but is prevented from receiving updates. To change the behavior of your application when a license expires, you can can add custom logic based on the values for the expires_at field.
License Archival
When you archive a license in the vendor portal, it is hidden in the default license search and becomes read-only. Archival does not affect the utility of license files downloaded before the change.
To expire a license, set an expiration date and policy before archiving. This is a convenience feature for how licenses are displayed in the vendor portal.
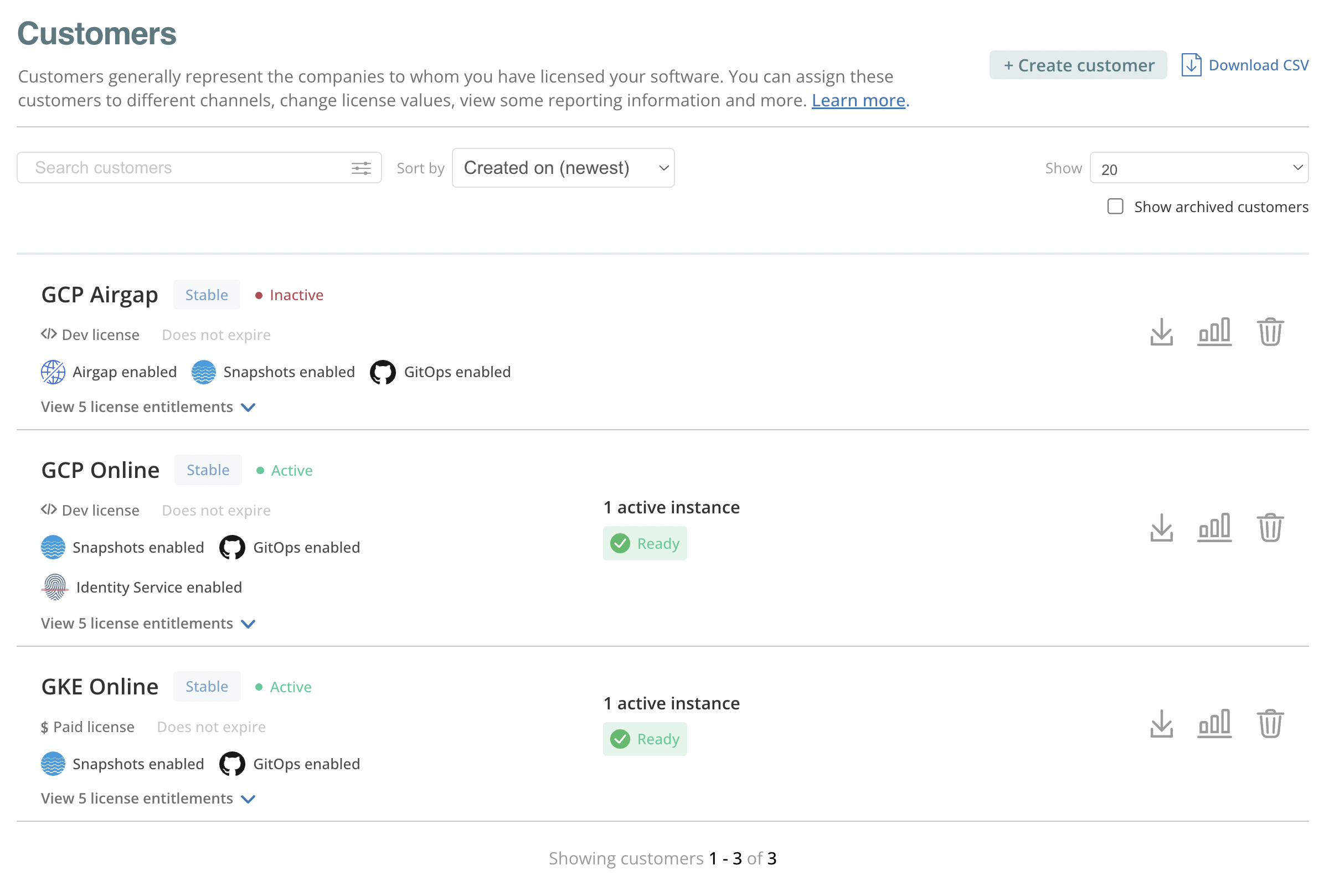
About the Customers Page
The Replicated vendor portal Customers page displays details about each customer license that you create, including the channel the customer is assigned, the type of license, the number of active application instances installed with the license, and more.
The following shows an example of the Customers page:
View a larger version of this image
From the Customers page, you can do the following:
- Create new customers
- Download a CSV file with details about each customer
- Download the license file for each customer
- Archive customers
- Click the Customer reporting button to view data about the active application instances associated with each customer on the Reporting page. See About the Customer Reporting Page below.
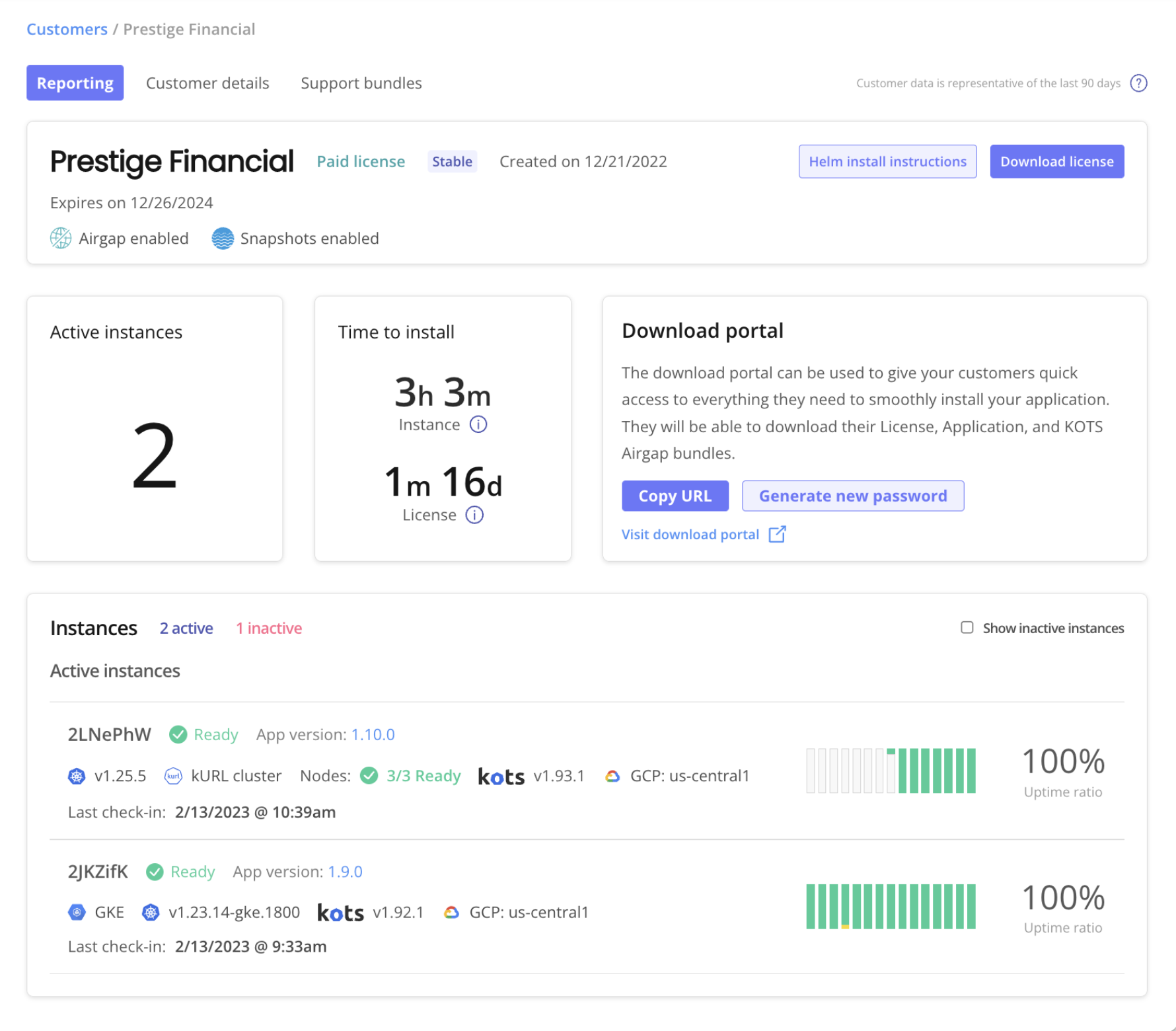
About the Customer Reporting Page
The Reporting page displays data about the active application instances associated with each customer. The following shows an example of the Reporting page for a customer:
View a larger version of this image
You can click any of the rows on the Reporting page to open the Instance details page. The Instance details page displays additional event data and computed metrics to help you understand the performance and status of each active application instance. For more information, see Viewing Instance Details.
The Reporting page displays the following details about each active instance:
The first seven characters of the instance ID
The status of the instance. Status is based on the status informers configured for the application. Possible statuses are Missing, Unavailable, Degraded, Ready, and Updating. For more information, see Resource Statuses in Displaying Application Status.
The application version
Details about the cluster where the instance is installed, including:
The Kubernetes distribution for the cluster, if applicable.
The Kubernetes version running in the cluster
Whether the instance is installed in a Kubernetes installer (kURL) cluster
(Kubernetes Installer Clusters Only) The number of nodes ready in the cluster
The following shows an example of the Nodes field for an instance installed in a Kubernetes installer cluster:

The app manager version running in the cluster
The cloud provider and region, if applicable.
Instance uptime data, including:
The timestamp of the last recorded check-in for the instance. A check-in is recorded when any of the following occur:
- The instance checks for updates. An update check can occur when a user clicks the Check for updates button in the Replicated admin console, or when the admin console runs an automatic update check. By default, the admin console runs automatic update checks every four hours. Users can modify or disable automatic update checks from the admin console. For more information, see Updating an Application in the Enterprise section.
- The status of an instance changes. For example, an instance can change from a Ready to Degraded status.
- (App manager v1.92 and later only) The instance completes an update to a new application version.
An uptime graph of the previous two weeks. For more information about how the vendor portal determines uptime, see Instance Uptime in Viewing Instance Details.
The uptime ratio in the previous two weeks.